- +91- 9820181545 / +91- 9870321970
- satiate.quality@gmail.com

All of the cells in the body have to be supplied with the necessary nutrients and oxygen. This is done via the arteries, which constantly distribute 'fresh' blood around the body. The Heart Pumps the blood into the arteries at high pressure. For the vessels to be able to withstand this high pressure. They have a strong musculature. exchange of the nutrients takes place in the very fine vessels called capillaries.
The veins transport the used blood back to the heart and to the organs which clean it and to the lungs which replenish it with oxygen. The walls of the veins are thinner than those of the arteries and the muscular layer is less pronounced, because the veins do not have to with-star~d as much pressure as the arteries.
Once it gets to the smallest capillaries, the pressure has largely dissipated. For the blood now to be transported back from the legs against gravity, the heart is no longer sufficient as a suction pump. Nature has equipped humans with various different mechanisms to help the blood to overcome the distance in height of around 1.5 metres from the feet back up to the heart.
Apart from the transport function for used blood, the veins also have a storage and temperature regulation function. When it is hot, the veins expand, thus taking up more blood so that it can be cooled on the surface of the skin.
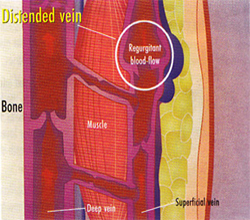
The veins run through the surface of our legs and collect blood from the layers of skin. This part is called the superficial venous system. From this system, the collected blood flows through connecting veins into the deep venous system, which is surrounded by muscles inside the leg. The deep venous system transports the blood back towards the heart by means of a muscle-pumping action.
The venous valves prevent the blood from flowing back down again. They function like non-return valves which only allow the blood to flow in one direction, namely in the direction of the heart. They look like smal~sails that are anchored around the vein wall and meet in the middle of the vein. If the blood flows upwards as a result of pressure from muscle pumping, the valves open. If the blood tries to flow back again due to the force of gravity, they close
As a result of their upright stance and a lifestyle with too little exercise, human beings are the only life forms that suffer from the widespread problem of diseased veins.
A lack of exercise and too much standing or sitting places considerable pressure on the venous system for many hours of the day. The muscle-pumping action no longer adequately supports the return transport of the blood. A genetic predisposition and increasing age or contributory hormonal factors as well as multiple pregnancies provide further unfavourable conditions.
The veins become increasingly distended. Due to their increased diameter, the valves can no longer close. The blood flows backwards and the superficial veins, which are not held in place by muscles or bone, become distended and appear as snaking varicose veins.
What are varicose veins? The word varicose is a medical term used to describe unnaturally and permanently distended veins. These veins will never regain their natural elasticity, which makes them unable to transport the blood properly.
The three main contributory factors involved in the development of varicose veins are as follows
| Anything that impedes the upward flow of blood from the legs: | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Tight Clothing |
| 2 | Pregnancy |
| 3 | Sports involving stomach pressure and heavy lifting. |
| 4 | Chronic coughing or constipation (straining causes strong backward pressure in the leg veins) |
| 5 | Prolonged sitting or crossing of the legs |
| 6 | Obesity |
| Anything that impedes or eliminates the muscle-pumping anion: | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Standing or sitting for prolonged periods |
| 2 | High heels |
| 3 | Paralysis |
The probability that the predisposition to vein diseases is inherited is high. Thus it is advisable to pay special attention to whether further members of the family are affected. A simple vein test can give
Tired legs, swollen ankles, tingling and itching, or stabbing pain in the legs may be the first signs of varicose veins developing, even before anything is to be seen.
Because the blood is no longer flowing back to the heart quickly enough, water from the veins escapes into the surrounding tissue. Swelling occurs, especially ground the ankles. If you notice such swelling every evening, regardless of what you were doing during the day, it is very likely that your veins are already damaged. If you can see swellings on the surface of your skin, you already have superficial varicose veins.
These are very fine blood vessels visible as a spidery pattern just under the surface of the skin. They are a few millimetres or centimetres in length and arranged in a fan pattern. Spider-veins rarely cause complaints and are mostly only a cosmetic nuisance. However, they can be a warning signal of varicose veins below.
If the vein wall becomes sob and distended, the venous valves no longer close properly. The blood stagnates. The veins give way even further. With time, this leads to the network of meandering blood vessels. Without the proper therapy, the varicose veins spread persistently. Some of the possible consequences are described here.
The signs of inflamed veins are a marked reddening, swelling, overheating and severe pain along the course of the vein.
If the return flow of blood to the heart is impaired, there is a greater danger of blood clots (thrombi) forming on the vessel walls. These clots block the vein and thus prevent the return flow of blood. Further damage to the venous system is incurred. The first signs are swelling of the lower leg, which may be accompanied by overheating, pain and a feeling of heaviness. Treatment by a doctor is imperative, as it can lead to a clot entering the lungs which can be a life threatening pulmonary embolism.
Because the oxygen-deficient blood in the veins is not transported away, the exchange of nutrients ant waste products is impaired. This leads to cells being seriously damaged and tissue dying off. Chronic wound! can be the result. Healing these type of chronic wounds is linked to addressing the cause of the coeditor namely distended varicose veins.
Venous diseases cannot be cured. Unfortunately, defective venous valves and distended veins cannot be returned to their previous condition. The two options available are invasive treatment, veins are sclerosed or surgically removed, and conservative therapy.
Conservative therapy is aimed at improving the condition by means of compression, exercise therapy and medication. Compression therapy is the basis for this. In some cases, compression bandages are necessary to begin with, in order to reduce the swelling of the leg.
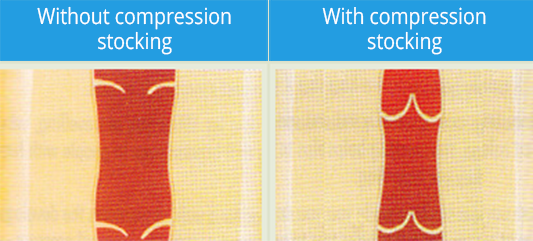
Both compression bandages and compression stockings reduce the diameter of the veins, so that the venous valves can close again, thus preventing the blood from flowing in the wrong direction - namely I away from the heart. After this type of therapy, but from the very beginning for most patients, modern medical compression stockings may be used to compress the tissues.
Medkal Compression stockings prevent new varicose veins from formir and keep existing venous disease under control. If venous disease is left untreated, it may become progressively worse and below Chronic. This is why it is particularly important to prevent deteriorating of Complications Consistently by wearing your Compression stocking
Additionol, valuable support for your veins con be provided by the right combination of measures. The compression stocking has fl ~mechonicolly" constrictive Stied Substonces such as horse chestnut extract hove on internal sealing effect on the vein woll.
contain horse chestnut extract and hove been specially designed for these who wear compression stockings. The mediven gel cools under the compression stocking during the doy. In the evening, the mediven cream gives the tired skin the necessary nutrients end skin^fare it needs for the next day. For optimum core 24 hours o day, mediven cream form em has been developed specially for dry, scaly skin.
It has to be sold there is no cure-oll pharmaceutical that cures varicose veins. However, medication con be used as o sensible supplement to therapy.
There ore vein tonics, i.e. medication that activates the muscles in the vein well and is aimed at accelerating return blood flow by increasing the elastic force of the vein. Oedemo protective agents ore designed to make the vein wall less permeable end thus prevent on increased collection of fluid in the tissue.
Both medications con support therapy with compression stockings end noticeably reduce the feeling of tension and heaviness in the legs. the most important and best known active substance is horse chestnut extract(aescin)
Your doctor will decide which treatment is necessary. Very smell spider-veins con be treated by loser. The loser beets the blood in the smell superficial veins end obliterates them.
Sclerosis involves o substance being injected into the diseased vein with a very thin needle. This leads to inflomotion end permanent closure of the diseased veins.
Larger varicose veins ore removed surgically. Today, the surgical methods hove been perfected to the degree thot 1~ the operation leaves virtually na visible scars end al healthy veins remain intact.
The single most important thing that ensures the success of therapy is sufficient exercise. All exercises end sports (walking, swimming, gymnostirs, cycling, cross-country shilling end dancing) thot keep the joints mobile end the leg muscles adive ore suitable here. Heavy lifting end jumping ore prohibited.
Special exercises hove been designed for vein patients. Vein exercise routines should be performed for at least 10 minutes twice o day to ochieve visible success. Ask your Theropist for instructions end aids, such as vein exercisers. This gymnastic bond makes it possible to do simple exercise especially to support the leg muscles.
mediven~ Nordic walking sticks is exceptionally suitable as on odjunctive measure for patients with venous end Iymphotic diseases.
It is easy to explain how o compression stocking works the pressure of the stocking constricts the diameter of the vein. The venous valves con close enjoin, thus reducing the amount of blood flowing bock down into the legs.
The smeller diameter of the veins means that the blood flows more quickly again, which prevents the formation of blood clots or thrombi. The medically prescribed drop in pressure from the foot upto the thigh accelerates the flow of blood bock to the heart. When the leg is moved, the stocking forms an external barrier for muscles, which makes for a more effective muscle pumping action
Wearing a compression stocking is generally not unpleasant, as is usually suggested. If you wear correctly fitted stocking, it immediately has a noticeable relieving effect and is a real treat for your legs
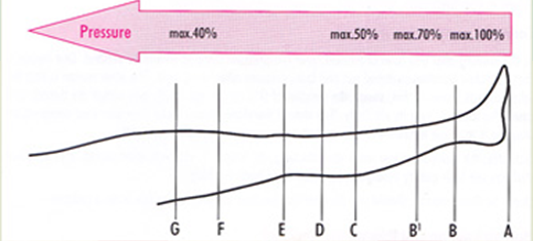
There is a simple rule of thumb for selecting the right stocking. The more severely the damage to thc venous system has progressed and the softer the leg tissue, the thicker and firmer the stocking must be.
The severity of a venous disease determines the pressure required. There are four recognised pressure classes:
| cc | Description | Pressure | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild compression | 18-21 mmHg | Prevention in the case of tired, heavy legs, caused by prolonged standing and during pregnancy |
| 2 | Moderate Compression | 23-32 mmHg | Pronounced varicose veins, swollen legs after flommotion of veios,after sderothempy or surgery, in the case of varicose veins during pregnancy |
| 3 | Strong Compression | 34-46 mmHg | After deep vein thrombosis constant leg swelling after a leg ulcer |
| 4 | Extra Strong Compression | 49 mmHg and above | very pronounced swelling lymphoedema |
If you have circulatory problems affecting the leg arteries or heart problems that are difficult to treat, you should consult your G.P. Caution is also necessary if you have loss of sensation due to diabetes.
Compression stockings have a defined pressure course from the heel to the thigh. This is the main difference from support stockings that are not subject to a standard. This means that only the compression stocking is medically effective.
Support stockings can be worn for prevention, but they do not provide the pressure of a compression stocking.
The "white stockings" in hospital are always used when a patient is confined to bed for prolonged periods. They are called anti-thrombosis stockings because they prevent blood clots from occuring when patients are Iying in bed. They are meant exclusively for resting legs and do not fulfil their purpose in mobile patients.
There is simply no alternative here if you want to achieve the best therapeutic results.
Your stockings are absolutely indispensable if you stand or sit a lot. When you're travelling, whether by car or plane, the stocking helps to prevent the blood clots that happen even to people with healthy veins when they are travelling.If you wear your stocking while you do your doily exercises or go for a walk, it promotes the development of muscle, as your muscles have to make an additional effort to overcome the external pressure.Put your compression stocking on in the morning directly after you have got up and had a shower, as your legs are not yet swollen at age.
In the evening after you have undressed, your compression stocking should be washed. One reason is that the fabric becomes stretched out and loses pressure aver being worn. The other reason is that the fabric collects flakes of skin, sweat, the remains of skin cream, etc. which may attack the threads and cause the fabric to lose its elasticity. You should therefore always make sure that your compression stocking is machine washable to ensure that it is as easy as possible to maintain.
Basically, the more omen you wash your stocking, the longer its elasticity is preserved. It is essential that you use high quality detergents for machine or hand washing.Under no circumstances should you dry your compression stocking in the sun or on a radiator.
Before putting on your compression stockings, it is best to take of F your watch and jewellery and wear rubber gloves to avoid damage to the fabric. The rubber gloves help to grip the fabric and make it much easier to hold and put on the stocking.
When putting on the stocking, avoid overstretching it by pulling it too hard, as it will then not fit your leg properly. As a consequence, the pressure distribution will not be correct and the stocking will slip down like a rubber band and gather around the back of your knee. This can lead to constriction.
The medi-Valet is a patented fitting aid for less mobile patients. It is also used by patients who . find it a more convenient way of putting on their stocking. It stretches the fabric for you, making it much easier to insert your foot. You then pull A on the handles gently to bring the stocking up to | the knee. The rest isn't so difficult, even for less mobile patients. The mediven valet is available I in various designs.
Physically active patients can remove the compression stocking by simply pulling it down and off the foot (on no account should it be rolled down).
Solution
for improved comfort and freshness Pediment supply cooling care products. The gel is applied in the morning before putting on the stocking and gives lasting freshness. There is also a handy spray that can be used from time to time, which soothes and cools the skin. The home remedy of spraying with water does cool the skin in the short term, but also tends to dry the skin.
Solution
Practice putting on your compression stocking with trained assistance. A stewing that has been overstretched slips down and will constrict your leg. If this is not the reason, your measurements must be checked again at your medical suppliers.
Solution
This is a common problem, since venous diseases are already accompanied by a poor supply of blood to the uppermost layers of skin. Special care products are available that have been specifically designed for compression therapy, such as those offered by mediven~.
Solution
Compression therapy must exert pressure on the leg. Since the ankle is furthermost from the heart, the pressure must be greatest here. You will get used to this feeling after a short while. Venous diseases are usually accompanied by pain and a tendency for the legs to swell. Almost all patients find that the feeling of the stocking on their legs provides considerable relief and prefer this to their previously tired and painful legs. Don't forget that the stocking keeps your leg fit and your blood in motion.
Solution
You can now obtain practical aids to help with putting on compression stockings. The mediven~ vale range offers you a good selection.The simplest aid is a pair of rubber gloves, which make it easier to put on the compression stockings because they adhere to the fabric and protect the stocking against damage from fingernails and jewellery
Tired, heavy legs and, omen at a young age, varicose veins: these are the results of too little exercise and long periods of standing end sitting.
All venous leg disorders are based on disturbed venous return from the legs to the heart. The medi Vein Exerciser actively supplements compression therapy; the ideal way of promoting venous return. Regular use of the Vein exerciser quickly and reliably activates the muscle pumps in the soles of the feet, ankles, calfs, knees and thighs. The result a demonstrable acceleration of venous return right up into the pelvis - which forms the basic of prevention and treatment of venous leg disorders. Post-thrombotic stiffness of the ankle joint is corrected carefully and virtually pain free.
The medi Vein Exerciser is used especially for
1. chronic venous insufficiency and its consequences
2. exercise therapy
3. immobilized patients.
The medi Vein Exerciser is a simple, practical exercise aid (e.g. comfortably in the evening on the couch or simply during o breaks.)
Below, we hove shown you 10 exercises as the foundation for your own personal "leg fitness programmer'. For more exercising tips please ask your trainer or doctor.
Do all exercises in a comfortable position, always making sure your back is straight. Start exercise 1 wit a gentle pull on the strap. After 10 rocking cycles to stretch the muscles and tendons correctly you ca gradually increase the tension until the muscles tighten.



